by Wendy Castro –
In September 2016, Yahoo! had a rather bad day: The Internet giant confirmed in public that it was hacked in 2014.
Data from at least 500 million user accounts1 was stolen, including email addresses, dates of birth, telephone numbers, and more. It was the largest known data theft in history. But it certainly wasn’t the only data breach that occurred that year. Every single year, hundreds of companies2 in the U.S. alone suffer a theft of data.
Plenty of jokes were made about the Yahoo! data breach. But if your company suffers a data breach it will be no laughing matter. Data breaches are quite costly.
According to a recent study3, “the average loss to the value of a brand ranged from $184 million to $332 million, depending upon the type of information that was compromised.” And the same study reports that nearly half of all companies have suffered reputational damage as the result of stolen information.
Keeping your organization’s information secure is obviously of critical importance, and project managers play a key role in that responsibility. Management’s commitment to information security helps to set the tone for the entire team.
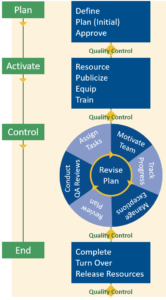
Keeping PACE with Information Security
RCG’s proprietary project management methodology, PACE, is an integral component of the project delivery framework at RCG. To assure the protection of our clients’ information, RCG’s Information Security Management System is integrated into our project management process.
The PACE methodology consists of four phases:
- Plan
- Activate
- Control
- End
We developed PACE primarily from the two industry standards for project management: the Capability Maturity Model Integrated framework (CMMI), and the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK).
Let’s take a closer look at each individual component of the PACE methodology to see how information security is implemented…
Plan Phase
This phase is where we define the project in terms of scope, assumptions, constraints, approach, deliverables, and roles and responsibilities. From a security perspective, this is when we determine and evaluate security requirements of the client. The planning phase is also the time to evaluate the sensitivity of the data involved.
The Plan phase involves determining whether the client requires any specific security requirements or protocols to be enforced. Some clients, for example, might require that specific tests for security be incorporated into testing plans.
During the Plan phase we factor the impact of security requirements into both the project cost estimates and schedule.
Activate Phase
The Activate Phase includes the validation and communication of the project structure, and the acquisition and development of project resources. This includes the human resources, the skills, facilities, equipment, and support for the project.
The Activate Phase launches the project, trains the project participants, and establishes the physical environment in which the project is conducted, and builds and maintains support for the project.
We developed a risk assessment questionnaire to help determine the security controls that will be required to implement and enforce for the project. The project environment is accessed to determine physical and network security needs.
A Cloud environment, for example, will have different security issues to address than a completely standalone local environment. Some clients will have specific security requirements that must be met, such as conducting all project work in a secure, dedicated workspace, or providing CCTV monitoring of team members.
As we onboard our project team, we assure that each team member has received information security awareness training. This is also the time to conform to any client-specific requirements for background checks of team members, and to make certain that each team member has submitted any required security-related documentation, such as NDAs.
During the Activate Phase, it’s also important to define communication protocols, and setup the appropriate communication tools. Different projects require different levels of communication security. Where chat messaging might be fine for one project, for example, it might be unacceptable for another project. This is also the time to define accepted media types and the standard approach for file transfers.
Control Phase
The primary focus of the Control Phase is to perform the tasks defined in the work breakdown structure as defined in the Plan Phase. This phase involves monitoring ongoing activities to assure that we’re conforming to all security protocols and guidelines that were defined during the Activate phase. Risk Treatment Plans are monitored and evaluated for effectiveness.
Any project changes that occur during this phase must conform to project security requirements. If any new team members are onboarded, for instance, they must conform to the project security requirements for team members: background checks, documentation, etc. Any change to the project environment must undergo management and security approval.
We also perform periodic access reviews during the control phase. The purpose of these reviews is simply to assure that only authorized people have access to project data and data repositories. For long-term projects spanning more than a year, the project manager ensures that all team members receive information security awareness training refreshers annually.
For development projects, secure code reviews are conducted and submitted to the RCG Chief Architect. The handling of data used in quality assurance testing is also monitored to assure that test data are protected and do not contain confidential personal information.
End Phase
During this phase, project success and customer satisfaction are measured. This is accomplished by comparing the actual project results against the goals defined during the Plan Phase. Actual project results are documented by capturing actual project effort and costs, and performing Lessons Learned.
As the project winds down, it’s important that no security-related loose ends are left dangling. During the end phase we make certain that all of the RCG team’s access to the client environment and systems is terminated.
All project data is securely archived and all project equipment is returned to the client as appropriate.
Certifications Lend Credibility
The certification RCG maintains, lends credibility to our commitment for upholding our clients’ information security to the highest possible standards.
One of these certifications is ISO 270014, which “specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an information security management system within the context of the organization. It also includes requirements for the assessment and treatment of information security risks tailored to the needs of the organization.”
RCG also maintains certification in PCI Data Security Standards5, which “offers robust and comprehensive standards and supporting materials to enhance payment card data security. These materials include a framework of specifications, tools, measurements and support resources to help organizations ensure the safe handling of cardholder information at every step.”
We employ independent, third-party auditors/assessors in maintaining these certifications: TÜV Rheinland6 for ISO 27001 certification, and SISA7 for PCI DSS certification.
It’s Serious Business
Information security is about the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of information — CIA. And if the leadership at your company is smart, they take information security just as seriously as the government organization bearing that same acronym of CIA.
RCG certainly takes the information security of our customers that seriously. We owe our customers no less.
Works Cited
1. CNN Business (2016, Sept 23) "Yahoo says 500 million accounts stolen" Retrieved from https://money.cnn.com/2016/09/22/technology/yahoo-data-breach/
2. Identity Theft Resource Center https://www.idtheftcenter.org/notified
3. Excelsior University https://www.excelsior.edu/page/national-cybersecurity-institute/
4. ISO/IEC 27001 https://www.iso.org/standard/27001
5. PCI Security Standards Council https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/standards/
6. TÜV Rheinland http://www.tuv.com/en/corporate/home.jsp
7. SISA https://www.sisainfosec.com/